Which of the following enzyme substrate combinations is matched incorrectly – Which of the following enzyme-substrate combinations is matched incorrectly? This question delves into the intricate world of enzyme specificity, where the precise pairing of enzymes and substrates governs countless biochemical reactions. Join us as we unravel the mysteries of enzyme-substrate matching, exploring the factors that influence their interactions and the applications that rely on their accuracy.
In this comprehensive guide, we will provide a detailed overview of enzyme-substrate combinations, identify mismatched combinations, and delve into the concept of enzyme specificity. We will also examine the factors affecting enzyme-substrate binding and discuss the experimental methods used to determine these combinations.
Finally, we will explore the diverse applications of enzyme-substrate matching, highlighting its significance in various fields.
Enzyme-Substrate Combinations: Which Of The Following Enzyme Substrate Combinations Is Matched Incorrectly
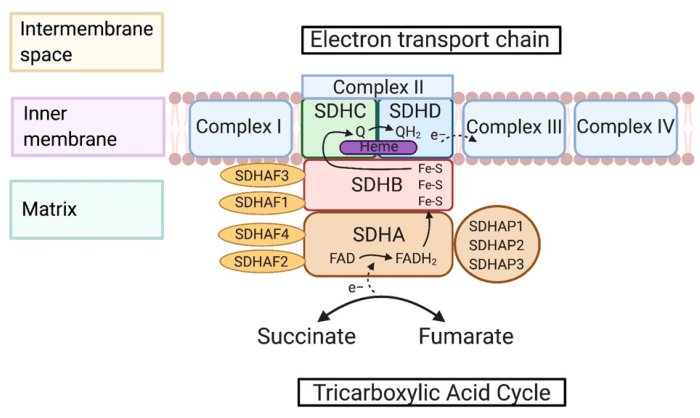
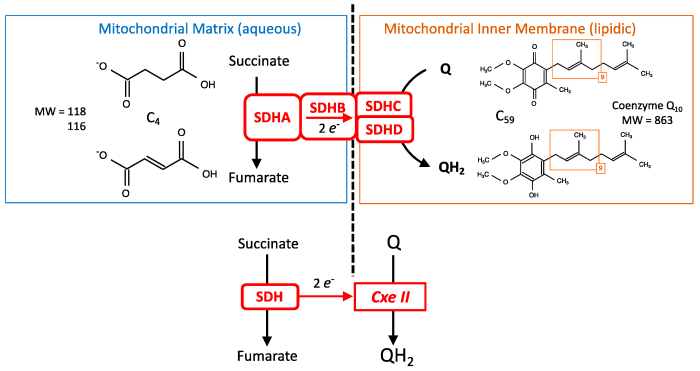
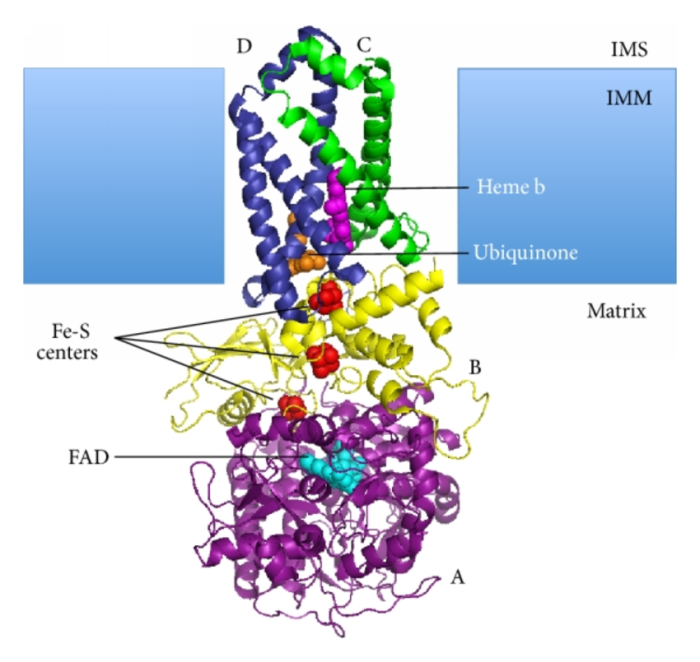
Enzyme-substrate combinations are the specific interactions between enzymes and the substrates they act upon. Enzymes are proteins that catalyze chemical reactions in living organisms, and substrates are the molecules that these reactions act upon. The correct matching of enzymes and substrates is essential for the proper functioning of biological systems.
Enzyme Specificity
Enzymes exhibit specificity in their interactions with substrates. This means that each enzyme is typically only able to catalyze a specific reaction or set of reactions involving a specific substrate or group of substrates. The specificity of enzymes is determined by the structure of the enzyme’s active site, which is the region of the enzyme that binds to the substrate and facilitates the reaction.
Factors Affecting Enzyme-Substrate Binding, Which of the following enzyme substrate combinations is matched incorrectly
The binding of enzymes to substrates is influenced by several factors, including:
- Molecular structure:The shape and chemical properties of the enzyme and substrate must be complementary for binding to occur.
- Temperature:Enzymes have an optimal temperature range at which they exhibit maximum activity. Deviations from this range can affect the binding of enzymes to substrates.
- pH:The pH of the environment can affect the ionization state of the enzyme and substrate, which can influence their binding.
- Concentration:The concentration of both the enzyme and substrate can affect the rate of binding.
Experimental Methods
Various experimental methods are used to determine enzyme-substrate combinations, including:
- Enzyme assays:These assays measure the activity of an enzyme in the presence of a specific substrate.
- Substrate specificity studies:These studies determine the range of substrates that an enzyme can act upon.
- Protein-substrate binding assays:These assays directly measure the binding of an enzyme to a substrate.
Applications of Enzyme-Substrate Matching
Accurate enzyme-substrate matching is essential for various applications, including:
- Biocatalysis:Enzymes are used in industrial processes to catalyze specific reactions, and accurate enzyme-substrate matching is crucial for optimizing these processes.
- Drug development:Enzymes are targets for drug development, and accurate enzyme-substrate matching is essential for designing drugs that specifically inhibit or activate specific enzymes.
- Diagnostics:Enzymes are used in diagnostic tests to detect the presence of specific molecules, and accurate enzyme-substrate matching is essential for ensuring the accuracy of these tests.
FAQ Summary
What is enzyme specificity?
Enzyme specificity refers to the ability of enzymes to catalyze specific chemical reactions, recognizing and binding to particular substrates.
Why is enzyme specificity important?
Enzyme specificity ensures the accuracy and efficiency of biochemical reactions, preventing unwanted side reactions and maintaining cellular homeostasis.
What factors affect enzyme-substrate binding?
Factors such as substrate structure, enzyme conformation, temperature, and pH can influence the binding affinity between enzymes and substrates.