An object rolls off a tabletop with a horizontal velocity, embarking on a journey governed by the laws of motion. This captivating phenomenon unveils the intricate interplay between horizontal and vertical motion, shaping the object’s trajectory and ultimately its impact with the ground.
As the object embarks on its journey, it carries with it an initial horizontal velocity, propelling it forward along a horizontal plane. Simultaneously, the height of the tabletop dictates the object’s initial vertical position, influencing its subsequent motion.
Initial Conditions
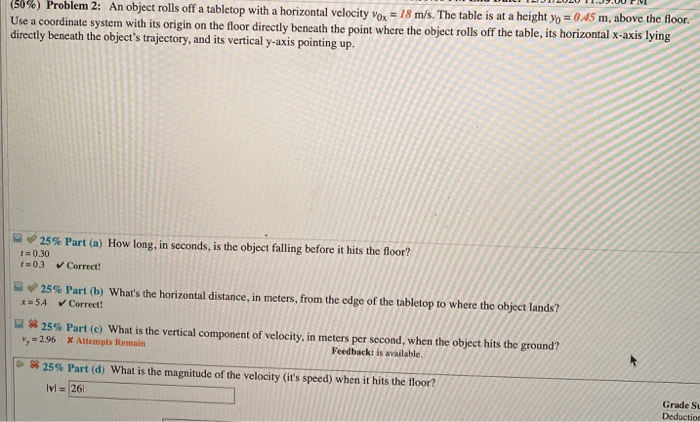
Before the object rolls off the tabletop, it has an initial horizontal velocity, denoted by v 0. This velocity is directed parallel to the surface of the tabletop. The height of the tabletop, denoted by h, is also an important factor in determining the object’s motion.
Equations of Motion

The object’s movement is governed by the following equations of motion:
- Horizontal displacement: x = v 0t
- Vertical displacement: y = -1/2gt 2+ h
- Time taken to hit the ground: t = √(2h/g)
where g is the acceleration due to gravity.
Trajectory of the Object
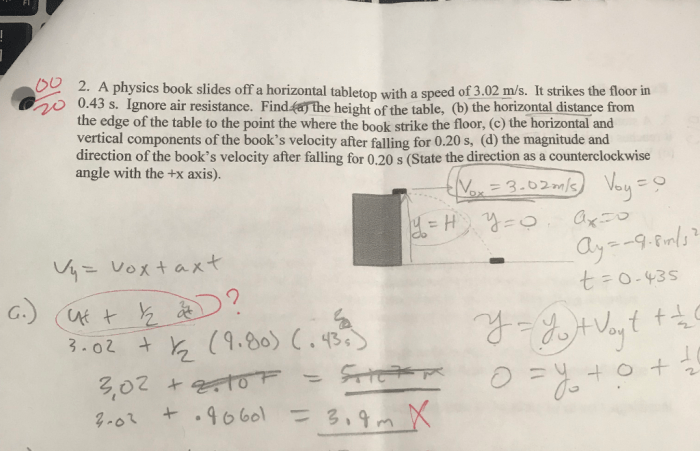
As the object rolls off the tabletop, it follows a parabolic trajectory. The shape of the parabola is determined by the object’s horizontal and vertical velocities. The horizontal velocity causes the object to move forward, while the vertical velocity causes it to fall downward.
Impact with the Ground: An Object Rolls Off A Tabletop With A Horizontal Velocity

When the object hits the ground, it experiences a force due to gravity and a force due to the ground. The force due to gravity causes the object to decelerate, while the force due to the ground causes it to stop moving.
The energy of the object is dissipated through heat and sound.
FAQ Compilation
What factors influence the trajectory of an object rolling off a tabletop?
The trajectory is influenced by the object’s initial horizontal velocity, the height of the tabletop, and the acceleration due to gravity.
How is the time taken for the object to hit the ground calculated?
The time taken can be calculated using the formula: t = sqrt(2h/g), where ‘h’ is the height of the tabletop and ‘g’ is the acceleration due to gravity.
What happens to the object’s energy upon impact with the ground?
Upon impact, the object’s kinetic energy is converted into other forms of energy, such as heat, sound, and deformation.