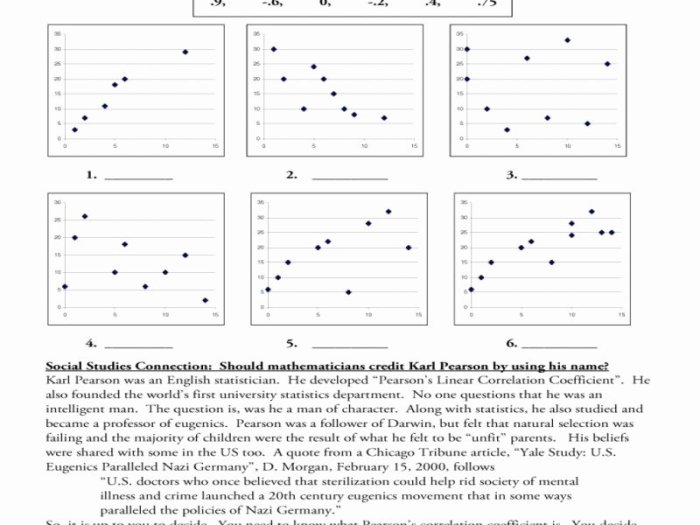
The correlation vs causation worksheet with answers provides a comprehensive guide to understanding the fundamental distinction between correlation and causation, empowering individuals to analyze and interpret data with greater precision. This resource delves into the nuances of these concepts, offering real-world examples and practical tips to avoid common pitfalls in drawing causal inferences.
Through engaging activities and thought-provoking questions, the worksheet fosters critical thinking and promotes a deeper comprehension of the relationship between variables. By utilizing this valuable tool, students and researchers alike can enhance their ability to discern true cause-and-effect relationships, leading to more informed decision-making and a more accurate understanding of the world around them.
Correlation and Causation: Correlation Vs Causation Worksheet With Answers
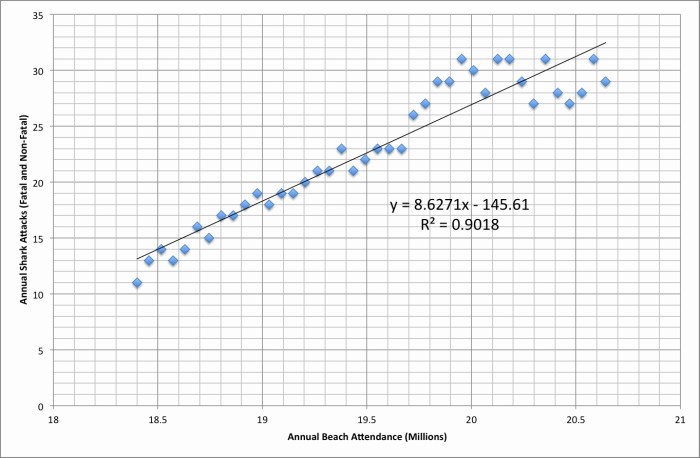
Correlation and causation are two terms that are often used interchangeably, but they have very different meanings. Correlation refers to a relationship between two variables, while causation refers to a relationship in which one variable causes the other.
It is important to be able to distinguish between correlation and causation because confusing the two can lead to incorrect conclusions. For example, if you observe a correlation between ice cream sales and drowning deaths, you might conclude that ice cream sales cause drowning deaths.
However, this is not necessarily the case. It is more likely that both ice cream sales and drowning deaths are caused by a third factor, such as hot weather.
Correlation vs. Causation Worksheet
The following worksheet can help you distinguish between correlation and causation:
- Identify the two variables in the relationship.
- Determine whether the relationship is positive or negative.
- Consider whether there is a third variable that could be causing both variables.
- Draw a conclusion about whether the relationship is likely to be causal.
Here is an example of how to use the worksheet:
- Variable 1: Ice cream sales
- Variable 2: Drowning deaths
- Relationship: Positive (as ice cream sales increase, drowning deaths also increase)
- Third variable: Hot weather
- Conclusion: It is unlikely that ice cream sales cause drowning deaths. It is more likely that both ice cream sales and drowning deaths are caused by hot weather.
Common Mistakes, Correlation vs causation worksheet with answers
There are a number of common mistakes that people make when trying to determine causation.
- Confusing correlation with causation.This is the most common mistake. Just because two variables are correlated does not mean that one causes the other.
- Ignoring other possible causes.When trying to determine causation, it is important to consider all of the possible factors that could be causing the observed relationship.
- Assuming that a cause-and-effect relationship is linear.In many cases, the relationship between two variables is not linear. For example, the relationship between smoking and lung cancer is not linear. The risk of lung cancer increases as the number of cigarettes smoked increases, but the risk does not increase at the same rate for all smokers.
It is important to be aware of these common mistakes when trying to determine causation. By avoiding these mistakes, you can increase the likelihood of drawing correct conclusions.
Real-World Examples
There are many real-world examples of how correlation and causation have been confused.
- The relationship between ice cream sales and drowning deaths.As mentioned above, the fact that ice cream sales and drowning deaths are correlated does not mean that ice cream sales cause drowning deaths.
- The relationship between gun ownership and crime rates.There is a strong correlation between gun ownership and crime rates. However, this does not mean that gun ownership causes crime. It is more likely that both gun ownership and crime rates are caused by other factors, such as poverty and inequality.
- The relationship between vaccines and autism.There is no evidence that vaccines cause autism. However, this has not stopped some people from believing that there is a link between the two. This belief is based on a now-discredited study that was published in 1998.
These are just a few examples of how correlation and causation have been confused. It is important to be aware of this issue so that you can avoid making the same mistakes.
Top FAQs
What is the primary objective of the correlation vs causation worksheet?
The primary objective of the correlation vs causation worksheet is to enhance individuals’ ability to distinguish between correlation and causation, enabling them to draw accurate inferences from data.
How does the worksheet facilitate the understanding of correlation and causation?
The worksheet employs engaging activities, real-world examples, and thought-provoking questions to illustrate the concepts of correlation and causation, making them relatable and accessible.
What are some common mistakes that the worksheet addresses in relation to causation?
The worksheet identifies common pitfalls in determining causation, such as mistaking correlation for causation, ignoring confounding variables, and drawing hasty conclusions based on limited data.
How can the worksheet contribute to improved decision-making?
By fostering a clear understanding of correlation and causation, the worksheet empowers individuals to make informed decisions based on evidence, rather than relying on spurious relationships.