Identify the ligament highlighted in the knee – Delving into the intricacies of the knee joint, this discourse unveils the crucial role of ligaments in maintaining its stability and preventing excessive movement. Through a comprehensive exploration of imaging techniques, ligament injuries, rehabilitation strategies, and preventive measures, we aim to illuminate the complexities surrounding the identification and management of ligamentous structures within the knee.
Anatomy of the Knee Joint: Identify The Ligament Highlighted In The Knee
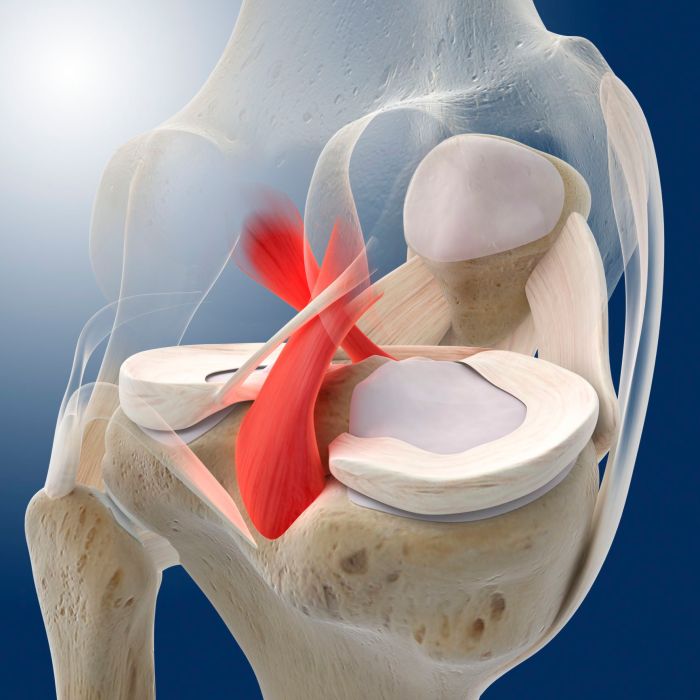
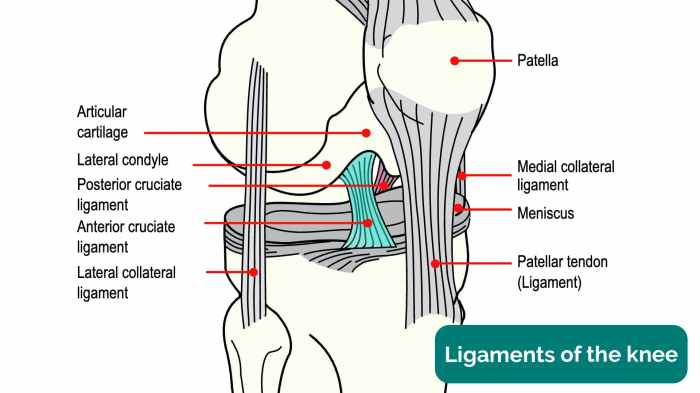
The knee joint is a complex and crucial structure that enables a wide range of movements, including flexion, extension, and rotation. It consists of three bones: the femur (thigh bone), tibia (shin bone), and patella (kneecap). The ends of these bones are covered with articular cartilage, a smooth, slippery tissue that reduces friction and allows for effortless movement.The
knee joint is stabilized by a network of ligaments, which are tough, fibrous bands of connective tissue that connect the bones and prevent excessive movement. The major ligaments of the knee include:
Imaging Techniques for Ligament Assessment
Various imaging techniques are employed to visualize and assess knee ligaments, each with its advantages and limitations:
-
-*X-rays
Provide a clear view of bones, but are less effective in detecting soft tissue injuries like ligament tears.
-*Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI)
Uses magnetic fields and radio waves to produce detailed images of ligaments and other soft tissues, making it ideal for diagnosing ligament injuries.
-*Arthroscopy
A minimally invasive procedure involving the insertion of a small camera into the knee joint, allowing direct visualization and assessment of ligaments.
Ligament Injuries
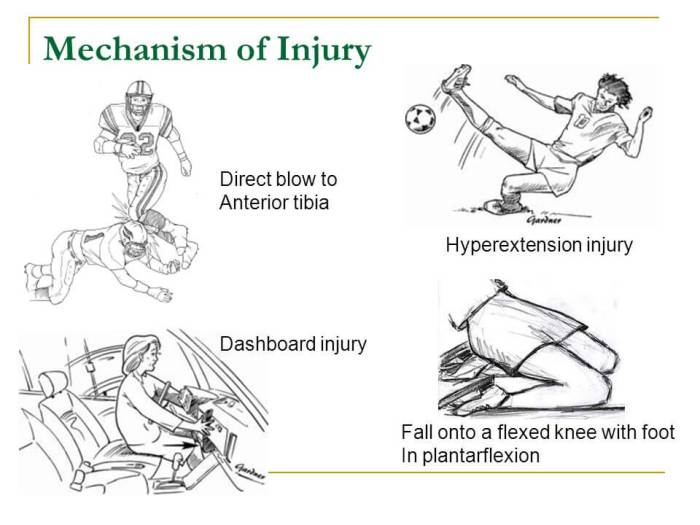
Ligament injuries range from mild sprains to severe ruptures, depending on the extent of damage to the ligament fibers. Sprains involve stretching or tearing of a ligament, while tears indicate a complete rupture. Ruptures are the most severe type of ligament injury and can significantly impair knee function.Common
causes of ligament injuries include:
-
-*Trauma
Direct impact or excessive force on the knee, such as in sports injuries or accidents.
-*Overuse
Repetitive stress or strain on the ligaments, often seen in athletes or individuals performing physically demanding tasks.
-*Age-related changes
Ligaments weaken with age, making them more susceptible to injury.
Rehabilitation and Recovery
Ligament rehabilitation aims to restore range of motion, strength, and stability to the knee joint. The principles of rehabilitation include:
-
-*RICE (Rest, Ice, Compression, Elevation)
Immediately after an injury, these measures help reduce swelling and pain.
-*Physical Therapy
Exercises guided by a physical therapist focus on regaining range of motion, strengthening muscles around the knee, and improving balance and coordination.
-*Gradual Progression
Rehabilitation is tailored to the individual’s progress, gradually increasing the intensity and complexity of exercises to prevent re-injury.
Prevention and Management, Identify the ligament highlighted in the knee
Preventing ligament injuries involves:
-
-*Proper Warm-up
Warming up before physical activity prepares the ligaments and muscles for movement.
-*Strengthening Exercises
Regularly strengthening muscles around the knee joint enhances stability and reduces the risk of ligament injuries.
-*Avoiding High-Risk Activities
Understanding and avoiding activities that put excessive stress on the knee can minimize the likelihood of injury.
Managing underlying conditions that increase the risk of ligament injuries, such as joint instability or muscle weakness, is also essential. Bracing and other protective measures may be recommended to prevent re-injury.
Q&A
What are the major ligaments of the knee?
The major ligaments of the knee include the anterior cruciate ligament (ACL), posterior cruciate ligament (PCL), medial collateral ligament (MCL), and lateral collateral ligament (LCL).
How are ligament injuries diagnosed?
Ligament injuries are typically diagnosed through a combination of physical examination, imaging techniques such as MRI or X-rays, and patient history.
What is the RICE protocol for ligament injuries?
The RICE protocol stands for Rest, Ice, Compression, and Elevation, and is commonly used to reduce pain, swelling, and inflammation in the immediate aftermath of a ligament injury.