Cycles Worksheet Carbon Cycle Answers embarks on an enthralling journey into the realm of carbon cycling, shedding light on the fundamental processes that govern the exchange of carbon within our planet’s ecosystems. From the intricate dance of photosynthesis and respiration to the vast carbon reservoirs that shape our environment, this comprehensive guide unravels the complexities of the carbon cycle with precision and clarity.
Delving into the depths of atmospheric carbon, we explore the factors that influence its concentration and the profound impact of human activities on its delicate balance. The role of the ocean as a carbon sink and the potential consequences of ocean acidification are meticulously examined, providing a deeper understanding of the intricate interplay between the carbon cycle and our planet’s oceans.
Carbon Cycle Overview
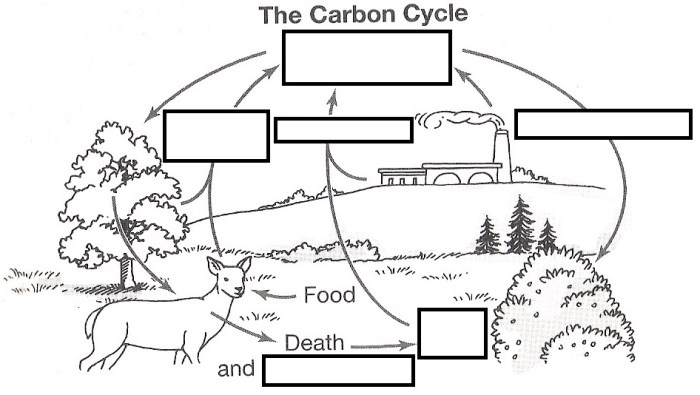
The carbon cycle is a fundamental biogeochemical process that involves the exchange of carbon between the Earth’s atmosphere, oceans, land, and living organisms. This intricate cycle plays a crucial role in regulating Earth’s climate and supporting life on the planet.
Photosynthesis and Respiration
Photosynthesis, a process performed by plants and certain microorganisms, utilizes sunlight to convert carbon dioxide and water into glucose (sugar) and oxygen. Respiration, on the other hand, is a metabolic process that breaks down glucose, releasing carbon dioxide as a byproduct.
Carbon Reservoirs
Carbon is stored in various reservoirs, including the atmosphere, oceans, terrestrial ecosystems, and geological formations. The atmosphere contains carbon dioxide, while oceans hold vast amounts of dissolved carbon in the form of bicarbonate ions and carbonate ions. Terrestrial ecosystems, particularly forests, store significant amounts of carbon in their biomass and soils.
Atmospheric Carbon
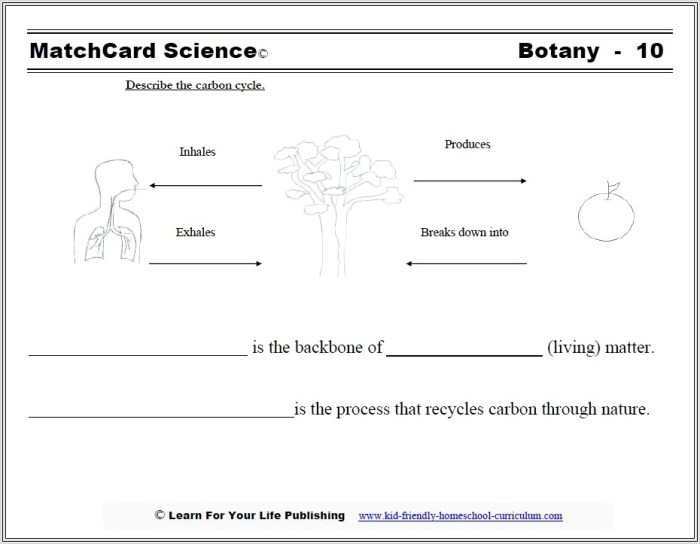
The concentration of carbon dioxide in the atmosphere is a crucial indicator of the Earth’s carbon balance. Atmospheric carbon levels have been rising steadily since the Industrial Revolution due to human activities, particularly the burning of fossil fuels.
Factors Influencing Atmospheric Carbon Levels
- Fossil fuel combustion
- Deforestation and land-use changes
- Oceanic absorption
- Terrestrial carbon sequestration
Human Impact on Atmospheric Carbon
Human activities have significantly contributed to the increase in atmospheric carbon dioxide levels, primarily through the burning of fossil fuels for energy production and deforestation. These activities release large amounts of carbon dioxide into the atmosphere, disrupting the natural carbon balance.
Oceanic Carbon
The ocean plays a vital role in regulating atmospheric carbon dioxide levels. Through a process known as the biological pump, marine organisms absorb carbon dioxide from the atmosphere and convert it into organic matter. This organic matter eventually sinks to the ocean floor, sequestering carbon for long periods.
Ocean Acidification
Increased atmospheric carbon dioxide levels lead to ocean acidification, a process that reduces the pH of seawater. Ocean acidification can have detrimental effects on marine organisms, particularly those with calcium carbonate shells or skeletons, as it can interfere with their ability to build and maintain their protective structures.
Terrestrial Carbon: Cycles Worksheet Carbon Cycle Answers
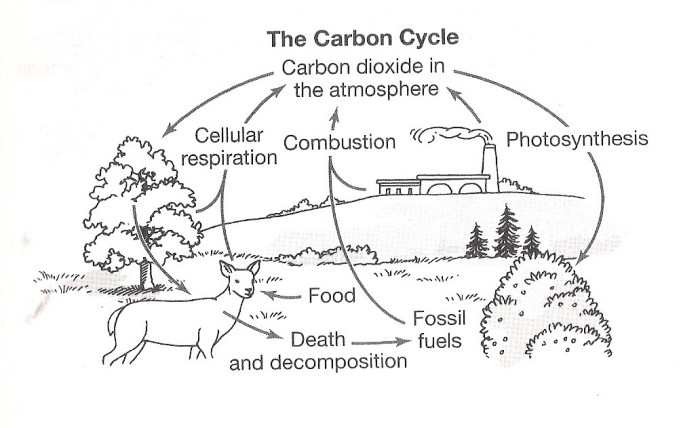
Terrestrial ecosystems, especially forests, act as significant carbon sinks. Trees and other plants absorb carbon dioxide during photosynthesis and store it in their biomass. Soils also play a crucial role in carbon sequestration, holding large amounts of organic carbon in the form of humus and other organic matter.
Impact of Deforestation
Deforestation and land-use changes release substantial amounts of carbon into the atmosphere. When forests are cleared, the stored carbon in trees and soils is released, contributing to the increase in atmospheric carbon dioxide levels.
Human Impact on the Carbon Cycle
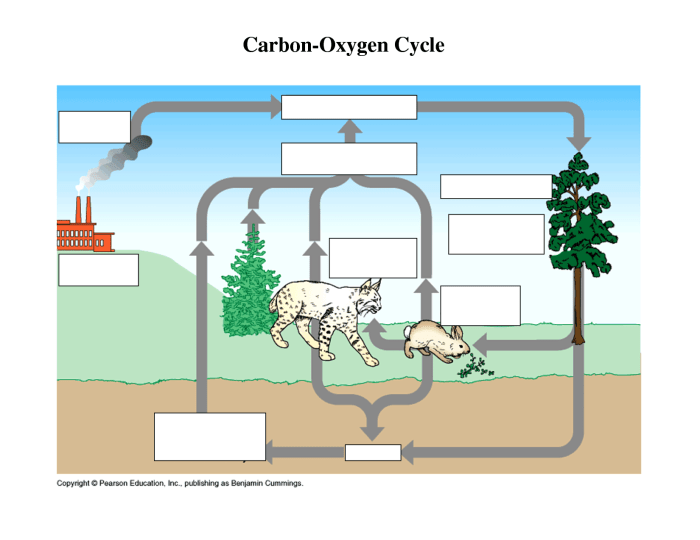
Human activities have significantly altered the carbon cycle, primarily through the burning of fossil fuels and deforestation. These activities release large amounts of carbon dioxide into the atmosphere, disrupting the natural carbon balance and leading to climate change.
Consequences of Increased Carbon Dioxide Levels
- Global warming
- Sea-level rise
- Ocean acidification
- Extreme weather events
Mitigation Strategies, Cycles worksheet carbon cycle answers
To mitigate human impacts on the carbon cycle, it is crucial to reduce carbon emissions through measures such as promoting renewable energy, improving energy efficiency, and implementing sustainable land-use practices. Additionally, carbon capture and storage technologies can help to remove carbon dioxide from the atmosphere.
FAQs
What is the primary mechanism responsible for carbon absorption in the ocean?
Phytoplankton and other marine organisms play a crucial role in absorbing carbon dioxide from the atmosphere through photosynthesis, converting it into organic matter.
How does deforestation impact terrestrial carbon storage?
Deforestation leads to a significant reduction in carbon storage capacity, as trees are a major reservoir of carbon. The removal of trees disrupts the carbon cycle, releasing stored carbon into the atmosphere.
What are the potential consequences of increased atmospheric carbon dioxide levels?
Elevated carbon dioxide levels contribute to climate change, leading to more frequent and severe weather events, rising sea levels, and disruptions to ecosystems.