Can EMT conduit be buried? The answer is yes, but it’s essential to follow specific regulations and best practices to ensure a safe and compliant installation. This comprehensive guide will delve into the intricacies of EMT conduit burial, covering everything from NEC requirements to soil conditions, depth, spacing, trenching, and backfilling.
Whether you’re a seasoned electrician or a DIY enthusiast, this guide will equip you with the knowledge and techniques to successfully bury EMT conduit.
EMT Conduit Burial Regulations
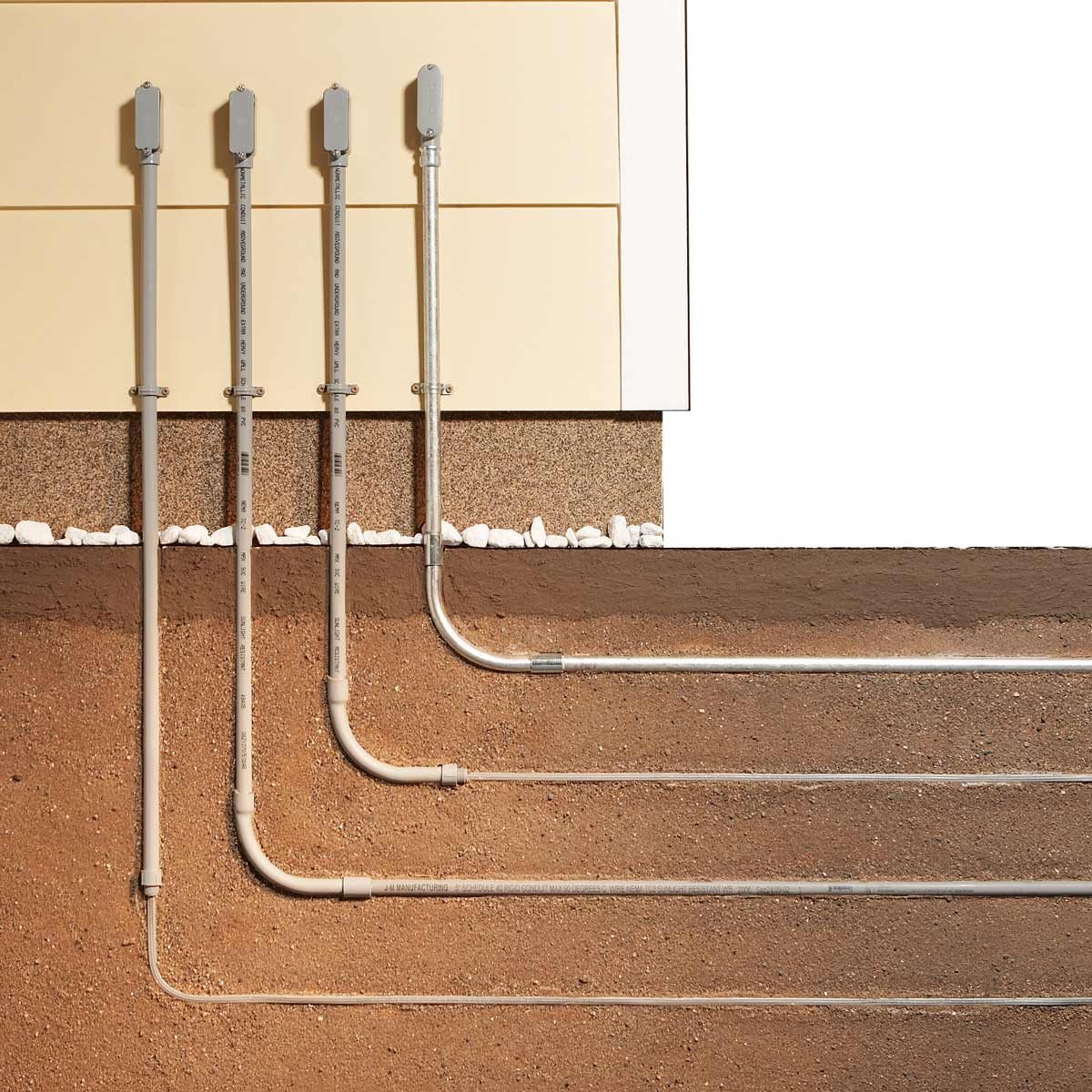
EMT (electrical metallic tubing) conduit can be buried underground, but it must be done according to specific regulations and codes. The National Electrical Code (NEC) sets forth the minimum requirements for burying EMT conduit, and local codes or ordinances may impose additional restrictions.
Acceptable Burial Methods
Acceptable methods for burying EMT conduit include:
- Direct burial in soil, provided that the conduit is at least 18 inches deep.
- Burial in concrete, provided that the conduit is encased in a minimum of 2 inches of concrete.
- Burial in a trench with other utilities, provided that the conduit is separated from the other utilities by at least 6 inches.
Unacceptable Burial Methods
Unacceptable methods for burying EMT conduit include:
- Burial in areas where the conduit will be subject to physical damage, such as from traffic or excavation.
- Burial in areas where the conduit will be exposed to corrosive substances, such as salt or chemicals.
- Burial in areas where the conduit will be subject to excessive heat, such as from a furnace or boiler.
Soil Conditions and Conduit Protection: Can Emt Conduit Be Buried

The type of soil in which EMT conduit is buried can significantly impact its lifespan and performance. Different soil conditions pose unique challenges, and understanding these conditions is crucial for ensuring the longevity of the conduit.
Soil conditions that can affect EMT conduit burial include:
- Soil pH:Acidic soils can corrode the conduit, while alkaline soils can damage the insulation.
- Soil moisture:Wet soils can promote corrosion and reduce the conduit’s insulation resistance.
- Soil compaction:Compacted soils can put pressure on the conduit, potentially damaging it.
- Soil composition:Soils containing rocks or other abrasive materials can damage the conduit’s outer surface.
To protect the conduit from corrosion and damage, several measures can be taken:
Conduit Protection
- Use of sand or gravel:Sand or gravel can be used to create a protective layer around the conduit, preventing direct contact with corrosive soils.
- Use of conduit wrap:Conduit wrap, such as electrical tape or heat shrink tubing, can provide an additional layer of protection against moisture and corrosion.
- Use of cathodic protection:Cathodic protection involves connecting the conduit to a sacrificial anode, which corrodes instead of the conduit, extending its lifespan.
By understanding the soil conditions and implementing appropriate protection measures, the longevity and reliability of EMT conduit buried underground can be significantly enhanced.
Conduit Depth and Spacing

Determining the proper depth and spacing for EMT conduits is crucial for ensuring their safety and longevity. These factors depend on several considerations, including soil conditions, conduit size, and potential hazards.
Minimum Burial Depth
The minimum burial depth for EMT conduit is typically 18 inches (457 mm) below the finished grade. This depth provides adequate protection from surface disturbances, such as digging or excavation, and helps prevent damage to the conduit and its contents.
Spacing Requirements
When installing multiple conduits in close proximity, it is important to maintain adequate spacing between them. This allows for proper heat dissipation, prevents interference with each other, and facilitates maintenance and repairs.
The National Electrical Code (NEC) recommends a minimum spacing of 6 inches (152 mm) between EMT conduits. This spacing ensures proper airflow and prevents overheating, which can compromise the integrity of the conduit and its contents.
When it comes to electrical wiring, it’s important to ensure that your conduits are properly installed and protected. While EMT (Electrical Metallic Tubing) is a common choice for electrical conduit, it’s important to note that it can only be buried underground if it is properly coated or protected from corrosion.
For more information on chemical compounds, check out this article on co3 aso4 2 compound name . Returning to the topic of EMT conduit, it’s crucial to ensure proper installation and protection to maintain its integrity and prevent any potential hazards.
Factors Affecting Depth and Spacing
The burial depth and spacing of EMT conduits can be affected by various factors, including:
- Soil Conditions:Soft or loose soil may require a deeper burial depth to provide stability and prevent damage.
- Conduit Size:Larger conduits may require a deeper burial depth to accommodate their increased weight and prevent bending or buckling.
- Potential Hazards:The presence of buried utilities, tree roots, or other potential hazards may necessitate a deeper burial depth or increased spacing.
Trenching and Backfilling

When burying EMT conduit, proper trenching and backfilling techniques are crucial to ensure its protection and longevity. Here are the steps involved:
Trenching
Dig a trench that is deep enough to provide the required cover over the conduit, typically between 18 and 24 inches. The width of the trench should be at least 6 inches wider than the conduit to allow for proper compaction.
Avoiding Damage
Use a shovel or trenching tool to dig the trench, avoiding sharp objects that could damage the conduit. When placing the conduit in the trench, handle it carefully to prevent bending or crushing.
Compaction and Drainage
Backfill the trench with soil or sand, compacting it in layers to ensure proper support for the conduit. Tamp the soil down firmly, but avoid overcompacting, which could damage the conduit. Slope the backfill slightly away from the conduit to promote drainage and prevent water from pooling around it.
Special Considerations

When burying EMT conduit in specific locations, it’s crucial to consider potential hazards and take necessary precautions. These locations include areas near trees, underground utilities, and other potential hazards.
Protecting Conduit from Trees, Can emt conduit be buried
Trees have extensive root systems that can damage buried conduit. To avoid this, bury the conduit at least 18 inches deep and at least 24 inches away from tree trunks. Consider using a conduit sleeve to provide additional protection against root penetration.
Protecting Conduit from Underground Utilities
Before digging, always call 811 to locate and mark underground utilities. Maintain a safe distance from these utilities when burying conduit, as per local regulations. Use caution when digging near gas lines, as even small sparks can ignite gas.
Protecting Conduit from Other Hazards
In areas with heavy traffic, consider burying conduit deeper or using a protective sleeve to prevent damage from vehicles. In areas prone to flooding, seal conduit openings to prevent water ingress.
Questions Often Asked
Is it permissible to bury EMT conduit directly in the ground?
Yes, EMT conduit can be buried directly in the ground, provided it meets the requirements of the National Electrical Code (NEC) and any applicable local codes.
What is the minimum burial depth for EMT conduit?
The minimum burial depth for EMT conduit is 18 inches in most cases. However, this depth may vary depending on local codes and soil conditions.
What precautions should be taken to protect EMT conduit from corrosion?
To protect EMT conduit from corrosion, it should be coated with a corrosion-resistant material, such as zinc or galvanized steel. Additionally, the conduit should be buried in well-drained soil and protected from exposure to moisture.